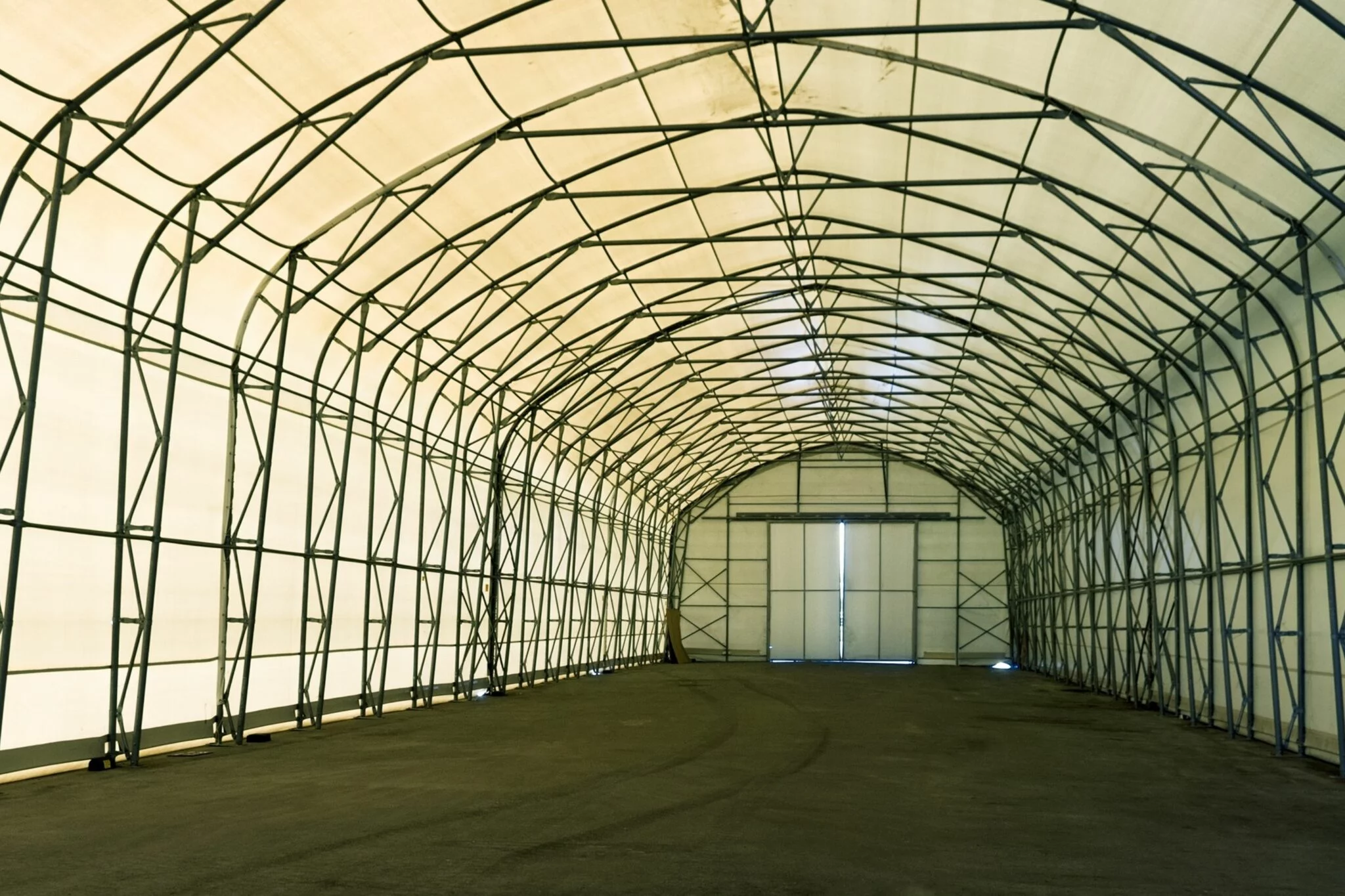
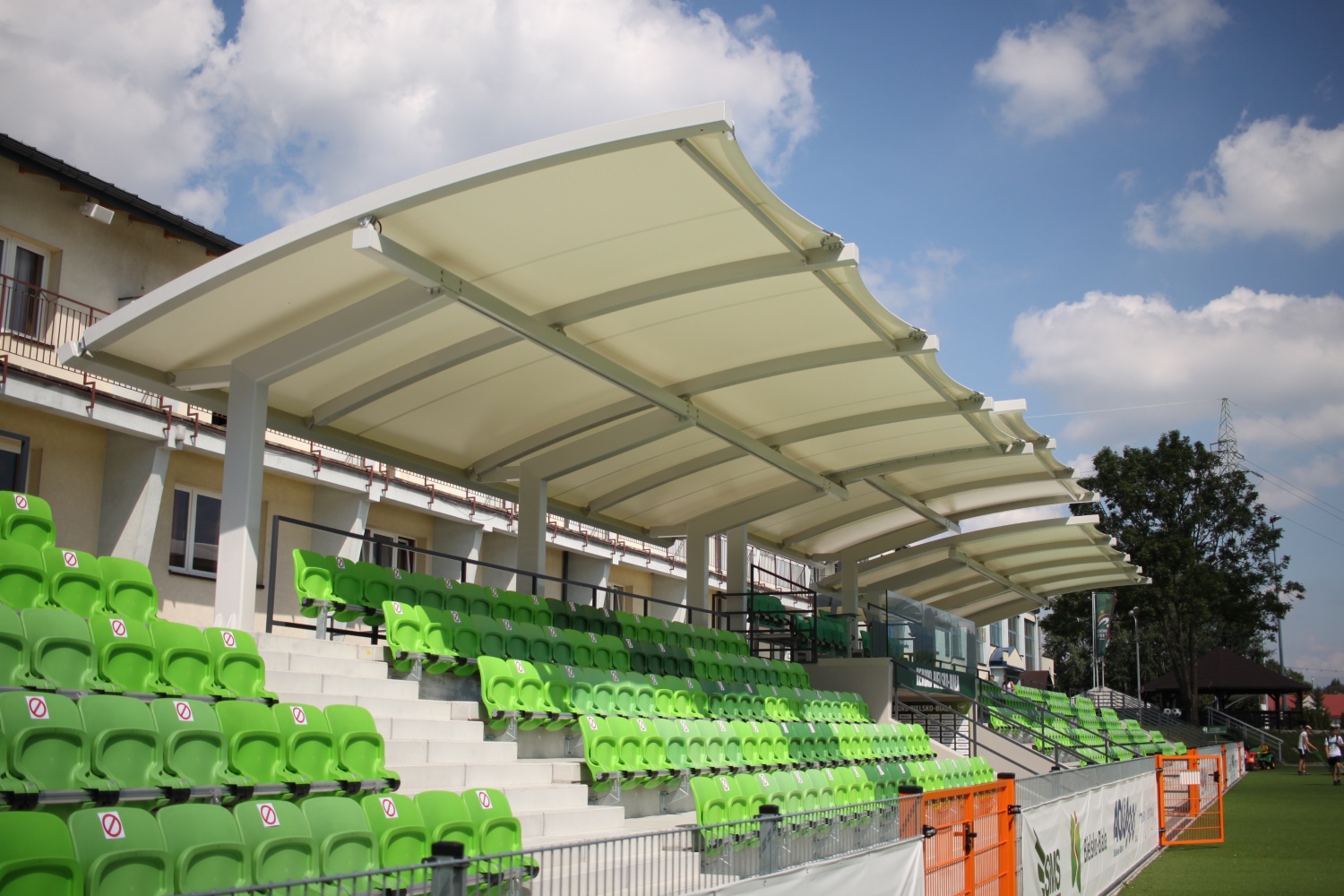
Jak wybrać odpowiednią tkaninę do hal namiotowych?
Wybór odpowiedniej tkaniny do hali namiotowej jest kluczowy, aby zapewnić jej trwałość, odporność na warunki atmosferyczne oraz ogólną wydajność. Tkanina, którą wybierzesz, bezpośrednio wpływa na żywotność namiotu, jego wygląd oraz zdolność do wytrzymywania różnych warunków środowiskowych. Przy dostępności wielu rodzajów tkanin namiotowych, ważne jest, aby zrozumieć unikalne cechy każdej z nich i jak pasują one do Twoich specyficznych potrzeb. W tym przewodniku omówimy różne rodzaje materiałów na pokrycia namiotów, czynniki, które warto rozważyć przy wyborze tkaniny namiotowej oraz najlepsze materiały do różnych zastosowań, od wesel po przechowywanie przemysłowe.
Rodzaje materiałów do hal namiotowych
Poliester
Poliester jest jednym z najpopularniejszych wyborów na tkaniny do hal namiotowych ze względu na doskonałą równowagę między trwałością a przystępnością cenową. Jest mocny, lekki i oferuje dobrą odporność na wodę. Poliester występuje w różnych splotach, takich jak oxford i ripstop, co zwiększa jego odporność na rozdarcia. Dodatkowo może być powlekany substancjami, takimi jak PVC, co poprawia jego wydajność w różnych warunkach atmosferycznych. Poliester to trwała tkanina namiotowa, stosowana zarówno w krótkoterminowych, jak i długoterminowych zastosowaniach.
- Wytrzymałość i trwałość: Poliester opiera się zużyciu, co czyni go idealnym do długotrwałego użytkowania.
- Odporność na wodę: Choć poliester sam w sobie jest wodoodporny, powłoki mogą jeszcze bardziej poprawić jego wodoodporność.
- Wszechstronność: Dostępny w różnych splotach i powłokach, oferuje elastyczność dla różnych potrzeb.
Poliester powlekany PVC
Poliester powlekany PVC podnosi trwałość poliestru o krok dalej, dodając warstwę polichlorku winylu (PVC), co czyni tkaninę bardziej wodoodporną, odporną na promieniowanie UV oraz trudnopalną. Ten materiał jest idealny do namiotów używanych w trudnych warunkach atmosferycznych lub tam, gdzie istotna jest ochrona przeciwpożarowa.
- Zwiększona wodoodporność: Powłoka PVC zapewnia, że tkanina może wytrzymać intensywne opady deszczu i zapobiegać wyciekom wody.
- Odporność na promieniowanie UV: Chroni namiot przed szkodliwymi promieniami UV, wydłużając żywotność tkaniny.
- Trudnopalność: Wiele tkanin powlekanych PVC spełnia normy bezpieczeństwa przeciwpożarowego, co czyni je idealnymi do wydarzeń publicznych i zastosowań przemysłowych.
- Jeśli zastanawiasz się nad zastosowaniem poliestru do pokrycia hal namiotowych kliknij tutaj.
Polietylen
Polietylen to ekonomiczna, lekka tkanina, często stosowana do materiałów hal namiotowych na czasowe lub krótkoterminowe projekty. Choć jest przyjazna dla budżetu, brakuje jej długoterminowej trwałości w porównaniu do poliestru i materiałów powlekanych PVC. Polietylen najlepiej sprawdza się tam, gdzie namiot nie będzie narażony na ekstremalne warunki lub długotrwałe nasłonecznienie, ponieważ jego odporność na promieniowanie UV jest stosunkowo niska.
- Lekkość: Łatwy w transporcie i montażu, idealny do tymczasowych schronień.
- Kosztowność: Idealny do projektów o napiętym budżecie lub krótkoterminowego użytkowania.
- Ograniczenia: Mniejsza trwałość i odporność na promieniowanie UV w porównaniu do innych tkanin.
- Tkanina ta idealnie nadaje się również na pokrycia namiotów wojskowych.
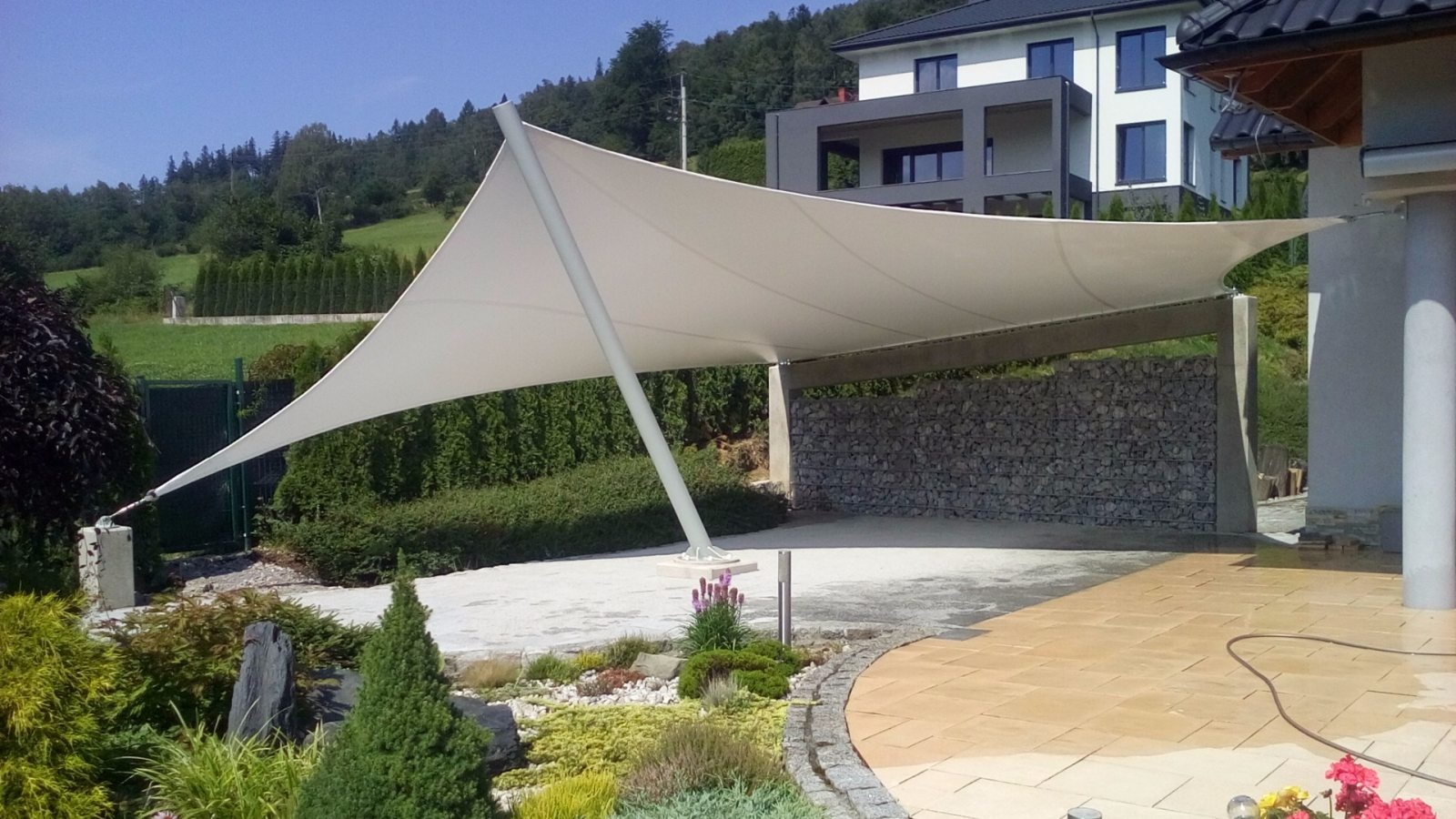
Płótno
Płótno to tradycyjna tkanina namiotowa znana ze swoich naturalnych, oddychających właściwości. Zapewnia doskonałą trwałość i odporność na warunki atmosferyczne, gdy jest odpowiednio zabezpieczone. Płótno często wybiera się ze względu na jego estetyczny wygląd, oferując klasyczny, rustykalny wygląd, co czyni je popularnym wyborem na namioty na imprezy. Jednakże, jest cięższe niż tkaniny syntetyczne, takie jak poliester lub polietylen, i wymaga więcej konserwacji, zwłaszcza w zakresie hydrofobizacji.
Tkanina idealna jeśli konfigurujesz tymczasowe zadaszenie.
Czynniki do rozważenia przy wyborze tkaniny do hal namiotowych
Wybierając odpowiednią tkaninę do hali namiotowej, kilka czynników powinno kierować Twoją decyzją:
- Trwałość i wytrzymałość: Upewnij się, że tkanina może wytrzymać zużycie, zwłaszcza jeśli namiot będzie często używany lub narażony na trudne warunki.
- Odporność na warunki atmosferyczne: Zastanów się nad warunkami pogodowymi, z jakimi namiot będzie musiał się zmierzyć. Tkaniny powlekane PVC oferują doskonałą ochronę przed deszczem i promieniowaniem UV, podczas gdy polietylen może wystarczyć na potrzeby tymczasowe.
- Trudnopalność: Dla bezpieczeństwa, zwłaszcza w miejscach publicznych lub przemysłowych, wybieraj tkaniny, które spełniają normy przeciwpożarowe.
- Oddychalność: Jeśli namiot będzie używany w gorących klimatach, oddychający materiał, taki jak płótno, może być bardziej komfortowy dla użytkowników.
- Estetyka i design: Wizualna atrakcyjność tkaniny jest istotna, zwłaszcza w przypadku namiotów na wydarzenia, takie jak wesela czy imprezy firmowe.
Najlepsze materiały do konkretnych zastosowań hal namiotowych
- Wesela i wydarzenia: PVC powlekany poliester jest doskonałym wyborem, łącząc trwałość z eleganckim wyglądem.
- Zastosowania przemysłowe i magazynowe: Trwałe i ekonomiczne materiały, takie jak polietylen lub powlekany PVC poliester, sprawdzą się w tych środowiskach.
- Schronienia tymczasowe: Polietylen jest idealny ze względu na lekkość i łatwość montażu.
Podsumowanie
Wybór odpowiedniej tkaniny do hali namiotowej zależy od Twoich specyficznych potrzeb, takich jak planowane zastosowanie, warunki pogodowe i budżet. Poliester i powlekany PVC oferują doskonałą trwałość i odporność na warunki atmosferyczne, co sprawia, że są one odpowiednie do długoterminowych instalacji lub wydarzeń wymagających solidnej wydajności. Polietylen jest z kolei lekką i ekonomiczną opcją na tymczasowe schronienia. Płótno, choć cięższe i wymagające więcej konserwacji, oferuje klasyczny wygląd i doskonałą oddychalność.
Jeśli rozważasz instalację hali namiotowej lub tymczasowego schronienia, skontaktuj się z nami, aby uzyskać fachowe porady i materiały najwyższej jakości.