ETFE Structure Norms and Certificates – What You Need to Know?
Planning a spectacular ETFE roof or facade? Excellent choice! This material offers incredible architectural possibilities. However, before your vision becomes reality, you must navigate the maze of documentation, norms, and certificates. This is where things get tricky. One incorrect document, one certificate covering a different system than the one in your project, can jeopardize the safety and legality of the entire investment.
Don’t worry, we won’t leave you to figure it out alone. This article is your practical guide to the world of requirements for ETFE structures. Step by step, in a way understandable to engineers and architects, we will show you what to pay attention to, how to read documents, and which mistakes to avoid. Think of this as a conversation with an experienced design team – because this is the knowledge, gained from Abastran projects, that we want to share with you.
What is ETFE and Why Choose It?
You probably know that ETFE is an advanced polymer. But what does this mean in practice for your project? First of all, you can forget about the limitations of heavy glass. ETFE film is ultra-light (weighing only 1% of the mass of its glass equivalent!), allowing for the design of roofing with enormous spans and minimal load on the supporting structure.
Its properties are impressive and solve many design challenges:
- Light Permeability: Up to 95%, meaning perfectly lit interiors and lower electricity bills.
- Durability: High resistance to UV radiation ensures the film does not yellow or become brittle. Its expected lifespan is over 30 years.
- Self-cleaning: A smooth surface with low free energy means rain washes away most dirt. No more costly roof cleaning!
- Flexibility: Allows for the creation of any organic shapes, from pneumatic cushions to single-layer tensioned membranes.
Thanks to these features, ETFE is ideal for roofing stadiums, atriums in shopping centers, zoos (like the famous Orientarium in Łódź), and modern office building facades. Our experience at Abastran shows that the key to success here is treating the structure as an integrated system, where the film, profiles, and fixings form an inseparable whole.
Key Standards You Must Know
The safety and quality of your structure are based on several fundamental standards. This is not optional reading; it’s your essential toolkit. You need to know what to demand from the contractor.
The foundation is the EN 1090 series of standards. This covers the execution of steel and aluminium structures, which form the framework supporting the entire ETFE membrane. Without compliance with this standard, the load-bearing structure cannot be legally placed on the EU market!
- EN 1090-1: Specifies requirements for conformity assessment, i.e., the procedure leading to the acquisition of CE marking.
- EN 1090-2: Specifies technical requirements for the execution of steel structures.
- EN 1090-3: Refers to technical requirements for aluminium structures.
Another pillar is fire safety. Here, the key standard is PN-EN 13501-2, which classifies construction products regarding fire resistance. However, for the film itself, the fire reaction classification will be more important (more on this shortly). Complementary system standards include: ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 3834 (welding quality), which demonstrate the contractor’s organizational and technological maturity.
How ETFE Certification Works in Practice?
The CE marking on a product is your guarantee that it has successfully passed the entire conformity assessment procedure. How does this work? The system manufacturer must implement and maintain Factory Production Control (FPC). This is nothing more than an internal supervision system that ensures each batch of the product has exactly the same declared properties.
The certification process, conducted by a notified body (e.g., Building Research Institute), includes an FPC audit and initial type testing in a laboratory. Only after successfully passing both stages does the manufacturer receive the certificate and can legally mark their product with the CE mark.
And now, the most important thing to remember: the CE certificate is issued for a specific, tested system, not for ETFE film as a raw material! This means the document covers a precisely defined set: film of a given thickness, profiles of a specific shape, and method of fixing. Changing even one element, e.g., using screws from a different supplier, formally invalidates the certificate for such a modified solution. At Abastran, we are uncompromising on this – compliance of the designed system with the certified one is an absolute priority for us.
Fire Resistance – How to Decipher REI and B-s1, d0 Markings?
Fire terminology can be confusing, so let’s clarify the facts. The REI classification refers to the fire resistance of entire building elements:
- R – Load-bearing capacity (the element will not collapse under load).
- E – Integrity (the element does not allow flames and hot gases to pass through).
- I – Insulation (the element does not heat up excessively on the side not exposed to fire).
A single ETFE film, being a fusible material, will not have an REI classification. For it, the fire reaction classification is key. The best and most frequently required is B-s1, d0. What does this mean?
- B – Material with limited flammability, with very limited contribution to fire.
- s1 – Very low smoke emission (s from smoke).
- d0 – No burning droplets (d from droplets).
In practice, this means that in the event of a fire, ETFE film melts and shrinks, creating natural openings for smoke and heat dissipation, but it does not sustain fire itself and does not create burning fragments that could spread the fire. This is its huge advantage compared to, for example, PVC.
How to Read Certificates to Avoid Costly Mistakes?
You’ve received a stack of documents from the contractor. Great. But how do you check if it’s not just junk? Here’s your checklist:
- Check the data: Do the manufacturer’s name, system name, and production site address on the certificate match the offer?
- Verify the scope: Does the certificate describe exactly the system (profiles, film thickness, fixings) that you have in your project? Compare the technical drawings from the certificate with those in the design documentation.
- Check the validity date: Make sure the certificate is current.
- Check the notified body: Does the institution that issued the document have the authorization to certify this type of product? You can check this in the EU NANDO database.
The most common mistake? Accepting a general technical data sheet for the film instead of the CE certificate for the entire structural system. Remember, you, as the investor or supervising designer, bear the ultimate responsibility. If in doubt, do not hesitate to ask the contractor questions or consult the documentation with an independent expert.
ETFE vs PVC and PTFE – Which Membrane to Choose for Your Project?
Material selection is always a compromise between price, aesthetics, and technical parameters. Let’s see how ETFE compares to the competition.
ETFE (Ethylene-tetrafluoroethylene) – Ideal when your priority is maximum transparency, lightness, durability, and freedom of form. It’s a premium solution, but its lifespan and low maintenance costs often offset the higher initial cost.
PVC (Polyvinyl chloride) – This is a more economical option. PVC-coated polyester fabric is flexible and available in many colors. Its downsides? Lower durability (15-20 years), susceptibility to dirt, and most importantly – worse performance in fire conditions (potential release of toxic smoke).
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) – A PTFE-coated fiberglass membrane is a master of fire resistance (class A2-s1, d0) and durability. However, it is an opaque material (only transmitting diffused light), heavier, and significantly more expensive. You choose it where fire regulations are extremely stringent and transparency is not crucial.
Understanding standards and the ability to read certificates is your superpower in the investment process. It is not unnecessary bureaucracy, but a tool for conscious quality and safety management. Equipped with this knowledge, you can confidently realize even the most ambitious architectural projects.
And if at any stage you feel you need support from experts who work with these technologies daily – remember that the Abastran team is at your disposal.
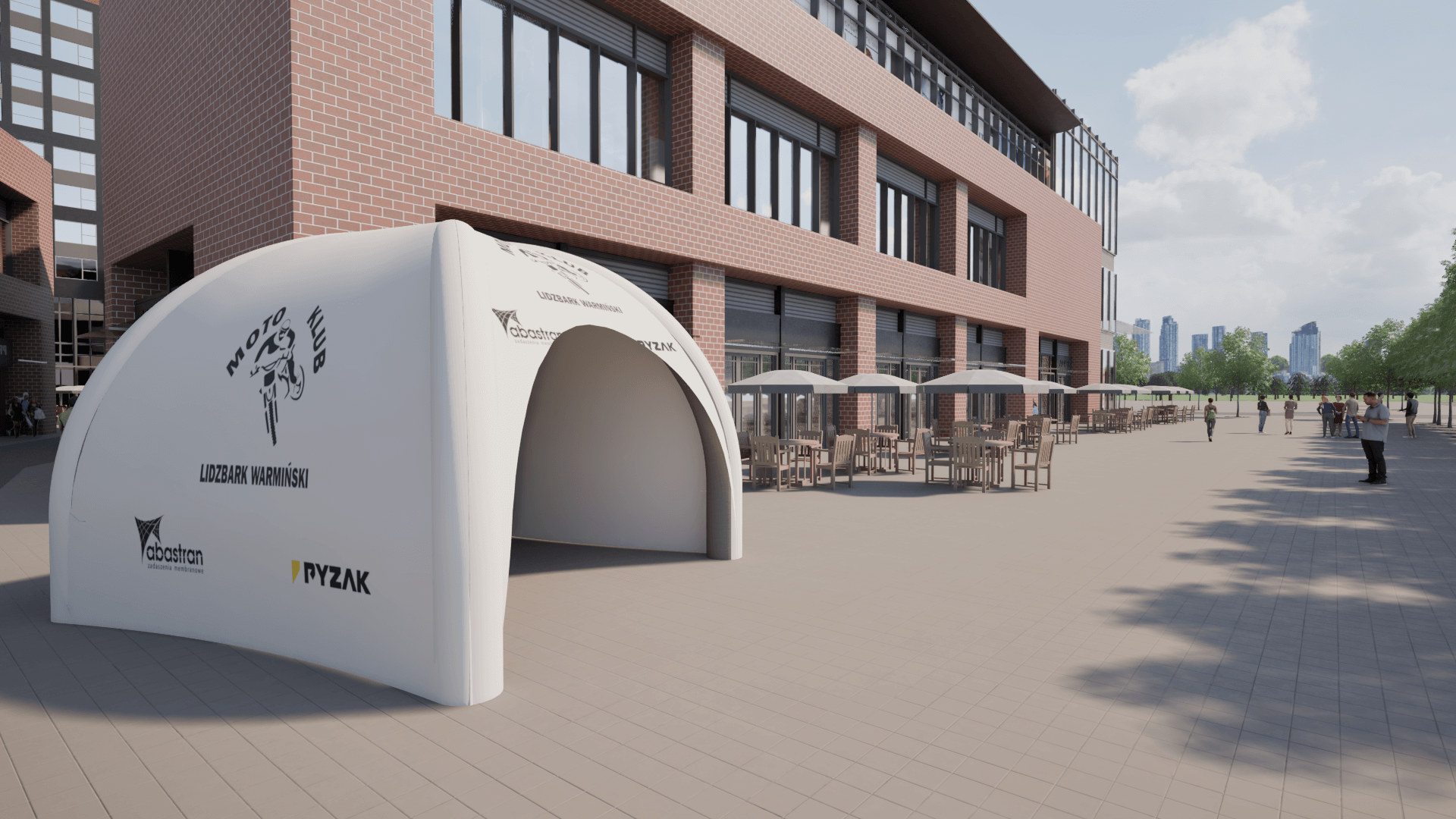

Advertising Tents as an Investment – How to Increase Brand Recognition at Events?
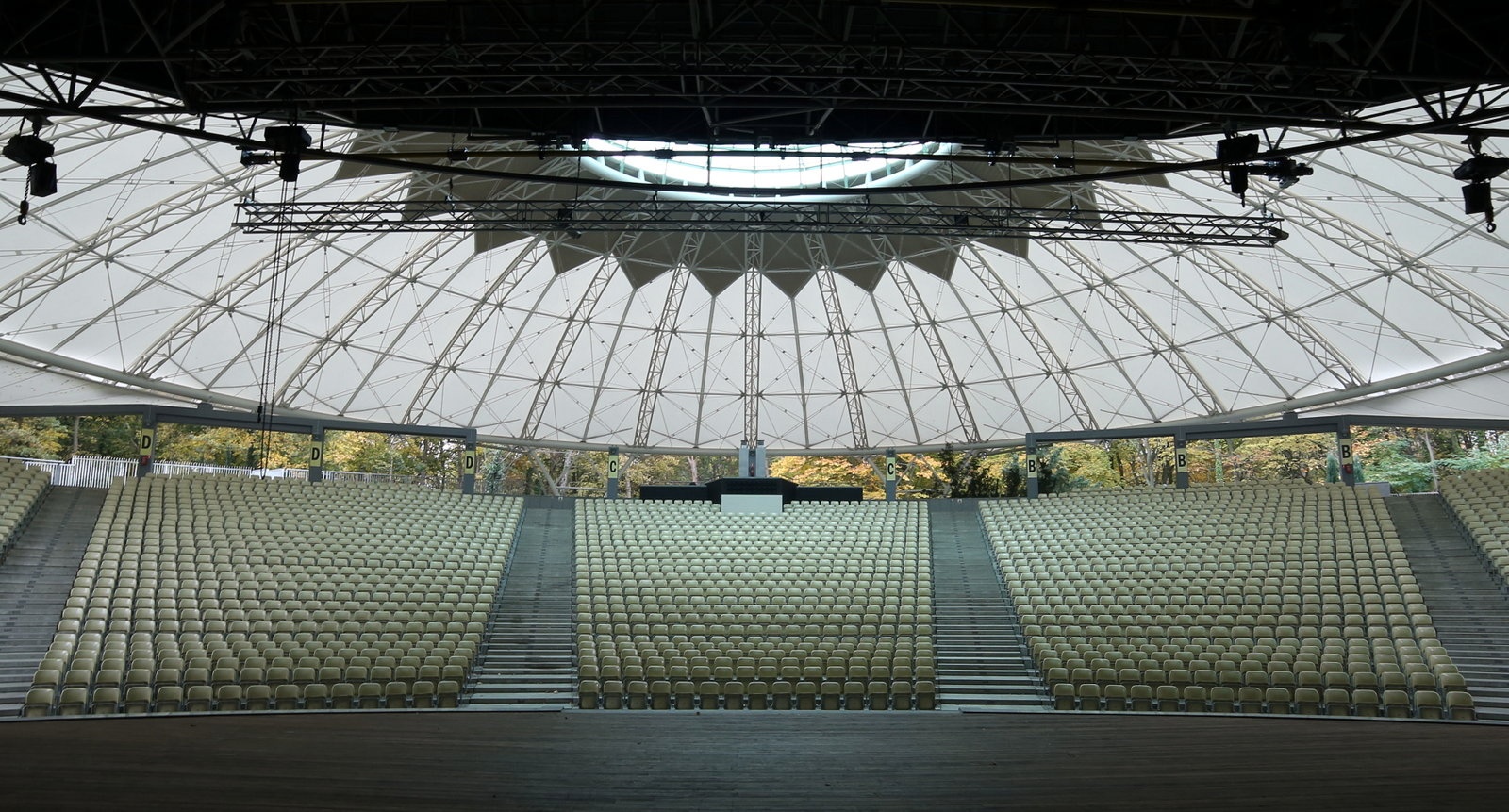
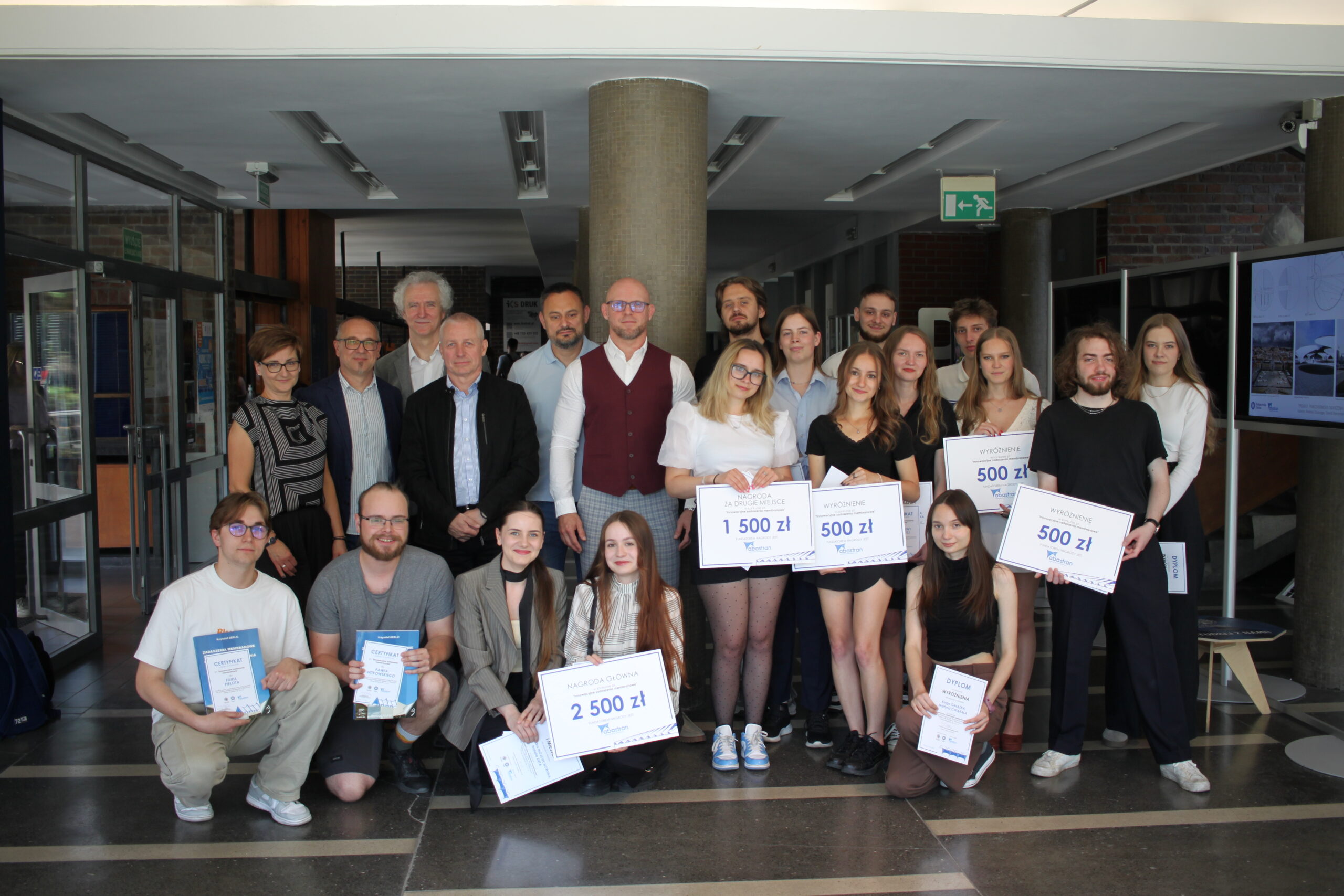


Competition for Innovative Membrane Roofing – Results and Inspirations
This year, we had the pleasure of organizing a competition together with the Faculty of Architecture at the Silesian University of Technology for 6th-semester students to design innovative membrane roofing. The award ceremony, held at the Faculty of Architecture in Gliwice, was the culmination of the young designers’ creative and technical journey.








